
Getty Images
If you’ve searched your name online in the last few years, you know what’s out there, and it’s bad. Alternately, you’ve seen the lowest-common-denominator ads begging you to search out people from your past to see what crimes are on their record. People-search sites are a gross loophole in the public records system, and it doesn’t feel like there’s much you can do about it.
Not that some firms haven’t promised to try. Do they work? Not really, Consumer Reports (CR) suggests in a recent study.
“[O]ur study shows that many of these services fall short of providing the kind of help and performance you’d expect, especially at the price levels some of them are charging,” said Yael Grauer, program manager for CR, in a statement.
Consumer Reports’ study asked 32 volunteers for permission to try to delete their personal data from 13 people-search sites, using seven services over four months. The services, including DeleteMe, Reputation Defender from Norton, and Confidently, were also compared to “Manual opt-outs,” i.e. following the tucked-away links to pull down that data on each people-search site. CR took volunteers from California, in which the California Consumer Privacy Act should theoretically make it mandatory for brokers to respond to opt-out requests, and in New York, with no such law, to compare results.
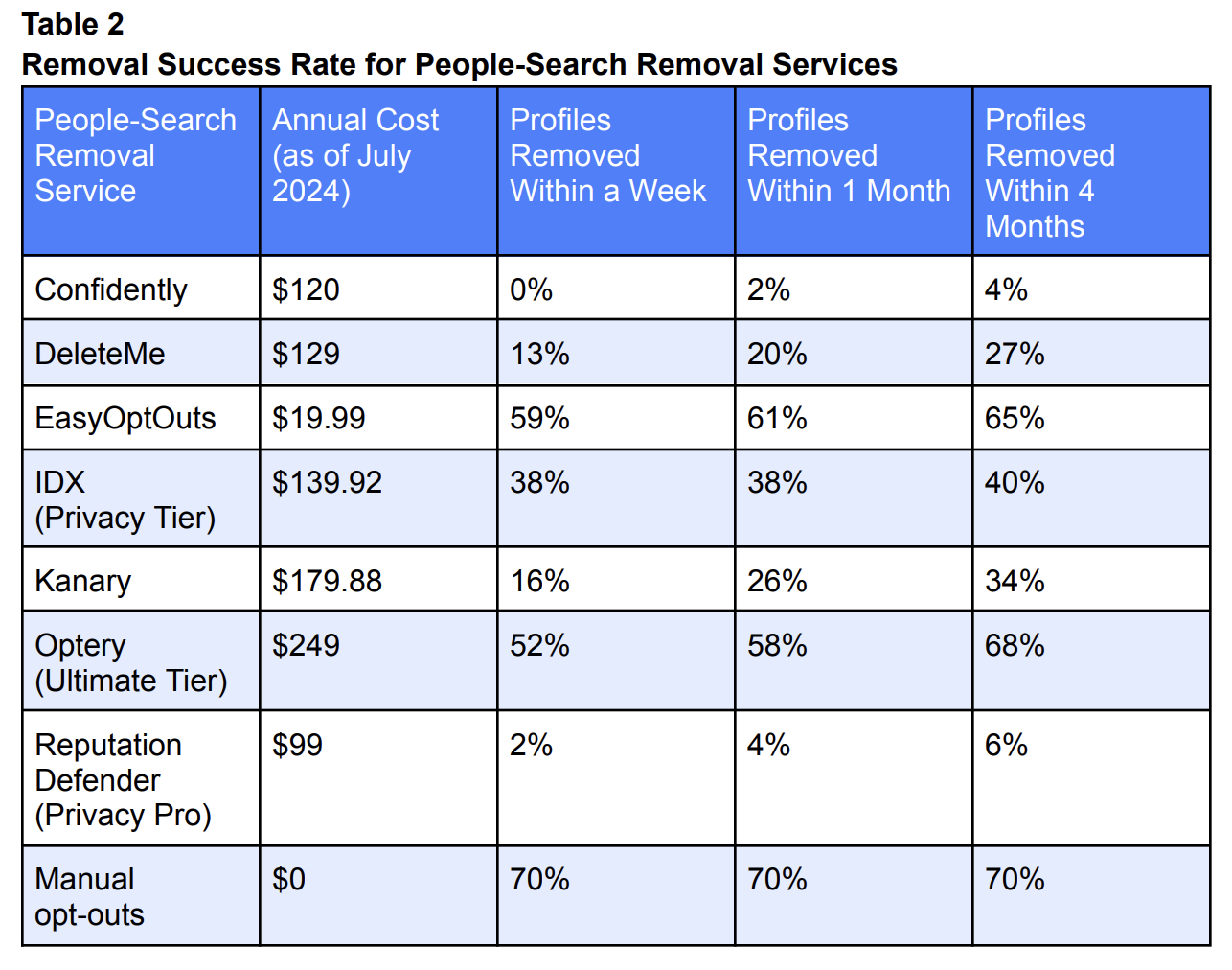
Table from Consumer Reports’ study of people-search removal services, showing effective removal rates over time for each service.
Finding a total of 332 instances of identifying information profiles on those sites, Consumer Reports found that only 117 profiles were removed within four months using all the services, or 35 percent. The services varied in efficacy, with EasyOptOuts notably performing the second-best at a 65 percent removal rate after four months. But if your goal is to remove entirely others’ ability to find out about you, no service Consumer Reports tested truly gets you there.
Manual opt-outs were the most effective removal method, at 70 percent removed within one week, which is both a higher elimination rate and quicker turn-around than all the automated services.
The study noted close ties between the people-search sites and the services that purport to clean them. Removing one volunteer’s data from ClustrMaps resulted in a page with a suggested “Next step”: signing up for privacy protection service OneRep. Firefox-maker Mozilla dropped OneRep as a service provider for its Mozilla Monitor Plus privacy bundle after reporting by Brian Krebs found that OneRep’s CEO had notable ties to the people-search industry.
In releasing this study, CR also advocates for laws at the federal and state level, like California’s Delete Act, that would make people-search removal far easier than manually scouring the web or paying for incomplete monitoring.
CR’s study cites CheckPeople, PublicDataUSA, and Intelius as the least responsive businesses in one of the least responsive industries, while noting that PeopleFinders, ClustrMaps, and ThatsThem deserve some very tiny, nearly inaudible recognition for complying with opt-out requests (our words, not theirs).

